Circuit Breaking Your Services
Fault Injection lets you see how the service mesh behaves when there are failures in network calls to a specific service. But how do you protect a service if it has overloaded or failing instances serving traffic? Ideally, you would like to identify an instance that is failing and prevent clients from connecting to it once it meets a certain threshold.
In OpenShift, an instance is equivalent to a Kubernetes pod running the microservice.
This concept is called Circuit Breaking - you set threshold limits for instances that run a microservice and if the threshold limits are reached, the circuit breaker “trips” and Istio prevents any further connections to that instance. Circuit breaking is another way to build resilient services in your service mesh.
In Istio, you can define circuit breaking limits using destination rules.
Define Threshold Limits
A circuit breaking rule has already been written for you for the user profile service.
View the destination rule in your favorite editor or via bash:
cat ./istio-configuration/destinationrule-circuitbreaking.yaml
Output (snippet):
...
trafficPolicy:
tls:
mode: ISTIO_MUTUAL
connectionPool:
http:
http1MaxPendingRequests: 1
maxRequestsPerConnection: 1
outlierDetection:
consecutiveErrors: 1
interval: 1s
baseEjectionTime: 10m
maxEjectionPercent: 100
...
The circuit breaking rule is only applied to v3 of the user profile service. The connection pool settings restrict the maximum number of requests to each instance to 1 (this makes it easier for you to trip the circuit for demo purposes). The outlier detection settings define the thresholds - an instance that fails once with a 50x error is ejected from the mesh for 10 minutes. You can read about the various settings in the Istio docs.
Deploy this circuit breaking rule:
oc apply -f ./istio-configuration/destinationrule-circuitbreaking.yaml
Trip the Circuit Breaker
First, route traffic evenly between v1 and v3 of the user profile service.
oc apply -f ./istio-configuration/virtual-service-userprofile-50-50.yaml
Send load to the user profile service:
while true; do curl -s -o /dev/null $GATEWAY_URL/profile; done
In another tab in terminal, kill the server running version 3 of the user profile service:
USERPROFILE_POD=$(oc get pod -l deploymentconfig=userprofile,version=3.0 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
oc exec $USERPROFILE_POD -- kill 1
Inspect the change in Kiali.
Navigate to 'Graph' in the left navigation bar.
If you lost the URL, you can retrieve it via:
echo $KIALI_CONSOLE
Switch to the 'Versioned app graph' view and change to 'Last 1m'. Change the 'No edge labels' dropdown to 'Requests percentage'.
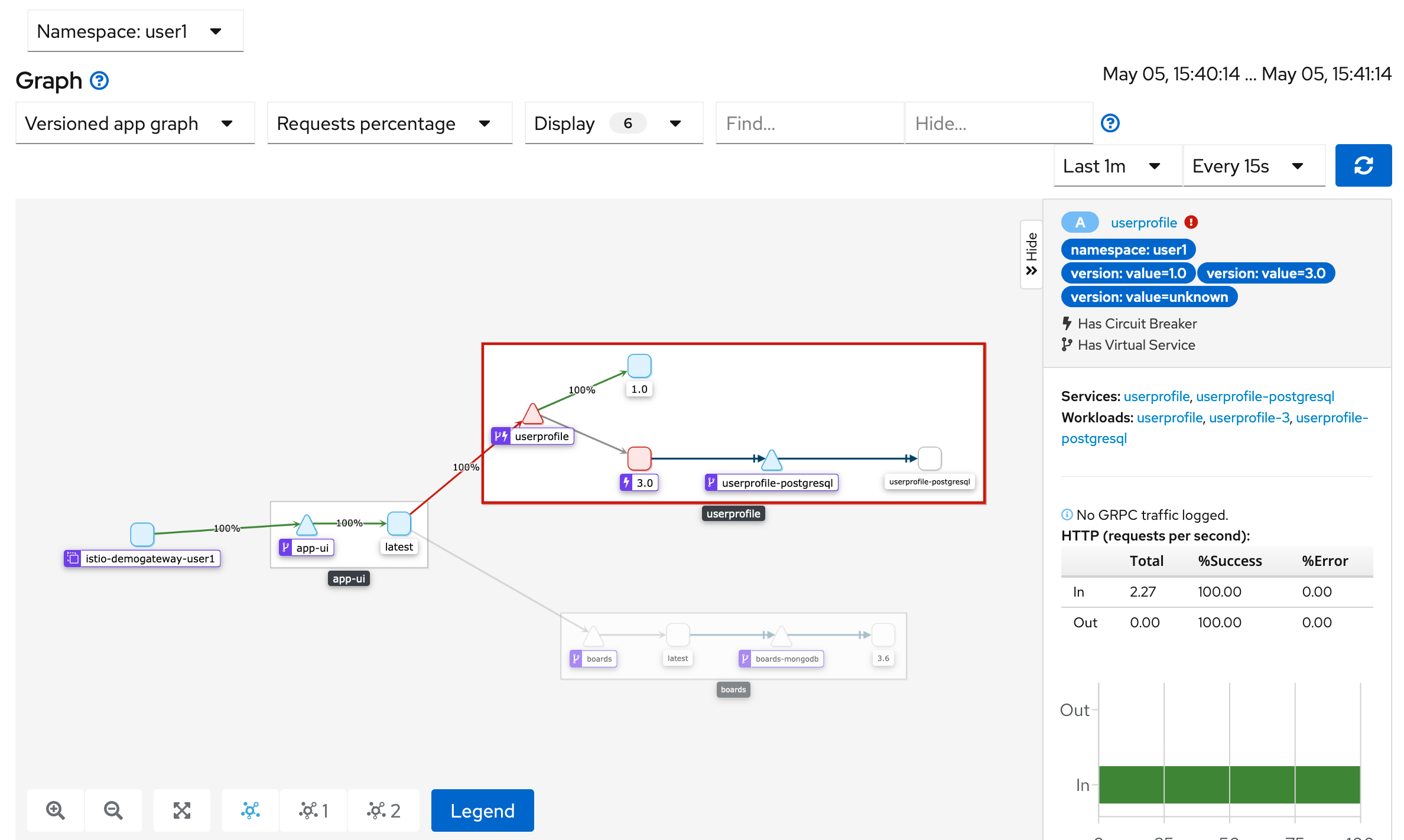
Traces to User Profile Service with Fault Delays
You should gradually see the percentage of traffic directed away from v3 to v1. The lightning icon indicates a circuit breaking rule, and the circuit breaker was tripped so traffic was routed to v1.
OpenShift will attempt to revive the server once the health check fails. If you see traffic rebalancing itself, run the command to kill the server again.
Clean up
Revert the changes you made before ending this lab.
oc apply -f ./istio-configuration/destinationrules-all.yaml
Summary
Congratulations, you configured circuit breaking in Istio!
A few key highlights are:
- Circuit breaking can build resiliency in the service mesh by tripping connections to an unhealthy service instance
- The threshold limits for tripping a circuit can be set in the Destination Rule
Workshop Details
| Domain |

|
|
| Workshop | ||
| Student ID |